© University of Liverpool 2019
FIELDWORKSAFETY


Hazards and risks
The Google Map on the right shows the satellite view of a stretch
of the coast near Abereiddy Bay in Pembrokeshire, South Wales.
Click on this Google Map to:
•
study the information shown on this map,
•
look at the photographs for Abereiddy Beach, Blue Lagoon
and Traeth Llyfn (the beach in the first large bay north of the
Blue Lagoon),
•
identify the hazards you would most likely encounter if you
were visiting these places on this stretch of the coastline,
•
decide the precautions you would take to reduce the risks at
Abereiddy, Blue Lagoon and Traeth Llyfn.

Fieldwork safety - test yourself
These quiz questions will test your understanding of Fieldwork Safety and your awareness of safety issues and the sorts of hazards that
you are likely to meet when working in the field.
For each item select the best possible option out of the choices listed.

Question 1
This shows a view of a disused mine in Cornwall.
The main hazard here is the:





Question 2
In upland areas the risk of
getting lost can be minimised by:




Question 3
This shows part of Bardon Hill Quarry in Leicestershire. Which
of the following items is not a hazard shown in this part of the
quarry?





Question 4
In an upland area, such as the area shown here, good quality
field clothing is essential and outer clothing must be:


Question 5
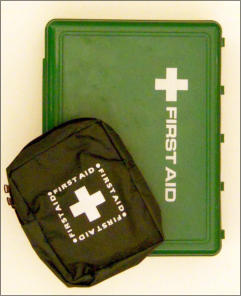
An essential item in a fieldwork first aid kit is:



Question 6
Tidal flats similar to those shown in this image hold risks because:





Question 7
Which of the following statements is in the Countryside Code?





Question 8
Always wear ear defenders when you are close to noisy plant in working quarries because there is risk of:





Question 9
A mobile phone may be useful when you are doing fieldwork, but remember that:




Question 10
Blasting occurs in most hard rock quarries like Bardon Hill Quarry
(shown in this image). When blasting takes place there is risk of
major physical injury resulting from:




Question 11
This is a view looking towards Llyn Ogwen in Snowdonia. If you
areundertaking fieldwork in this area it is always essential to wear:





Question 12
There is special risk in military training areas in coastal areas of:




Question 13
When you are working in upland areas it is essential that you:




Question 14
The International Distress Signal is:





Question 15
This photograph shows a coastal area near Amroth,
Pembrokeshire. The main hazard here is the:





Question 16
Insect bites can be a problem when working in the field, particularly
in northern latitudes and in upland or marshy areas. The best
precaution to take to prevent or reduce the risk of harm is to:




Question 18
Quicksand is a hazard in some coastal areas. If you get stuck in quicksand the first thing that you should do is:
Question 17
When you are doing fieldwork in coastal areas and are likely to be working on wavecut
platform like the one illustrated here you should always plan to work:









Question 19
Wherever possible you should avoid crossing a river, especially if you
are alone. If it is essential to ford or cross a river you should loosen the
shoulder straps and undo the waist strap of your rucksack because:





Question 20
If you are working in a quarry like the quarry shown in this image you must:







Next Steps
The task of identifying hazards does not cover all eventualities. When you are in the filed you are urged to beware of your surroundings at all times,
to take care and to use common sense.
Remember:
•
If you are working alone or in a small group on the coast that you must leave at your base a note of your field location and expected time of
return.
•
You must enquire about local conditions.
•
You need to check the local weather forecast and local tide tables.
•
In rough weather conditions tides may be higher than published in tide tables.
•
Recognise there are risks associated with a range of hazards encountered when undertaking fieldwork in coastal areas and take appropriate
measures to reduce these risks.
•
You must never take unnecessary risks.
•
You must ensure you have appropriate clothing, footwear, equipment and food with you in the field.
Hazards and precautions to reduce risk
Eight of the hazards in Abereiddy Bay are shown in the boxes below.
Click on each hazard and check that you identified the precaution you would take to reduce risk.














© University of Liverpool 2019
FIELDWORKSAFETY


Hazards
The Google Map on below shows the satellite view of a stretch of the coast near Abereiddy Bay in
Pembrokeshire, South Wales.
Click on this Google Map to:
•
study the information shown on this map,
•
look at the photographs for Abereiddy Beach, Blue Lagoon and Traeth Llyfn (the beach in the
first large bay north of the Blue Lagoon),
•
identify the hazards you would most likely encounter if you were visiting these places on this
stretch of the coastline,
•
decide the precautions you would take to reduce the risks at Abereiddy, Blue Lagoon and
Traeth Llyfn.

Hazards and precautions to reduce risk
Eight of the hazards in Abereiddy Bay are shown in the boxes below.
Click on each hazard and check that you identified the precaution you
would take to reduce risk.








Next Steps
The task of identifying hazards does not cover all eventualities. When you are in the filed you are
urged to beware of your surroundings at all times, to take care and to use common sense.
Remember:
•
If you are working alone or in a small group on the coast that you must leave at your base a
note of your field location and expected time of return.
•
You must enquire about local conditions.
•
You need to check the local weather forecast and local tide tables.
•
In rough weather conditions tides may be higher than published in tide tables.
•
Recognise there are risks associated with a range of hazards encountered when undertaking
fieldwork in coastal areas and take appropriate measures to reduce these risks.
•
You must never take unnecessary risks.
•
You must ensure you have appropriate clothing, footwear, equipment and food with you in
the field.


Fieldwork safety - test yourself
These quiz questions will test your understanding of Fieldwork Safety and your awareness of
safety issues and the sorts of hazards that you are likely to meet when working in the field.
For each item select the best possible option out of the choices listed.

This shows a view of a disused mine in Cornwall. The main hazard here is the:




Question 1
Question 2

In upland areas the risk of getting lost can be minimised by:




Question 3

This shows part of Bardon Hill Quarry in Leicestershire. Which of the following
items is not a hazard shown in this part of the quarry?




Question 4

In an upland area, such as the area
shown here, good quality field clothing
is essential and outer clothing must be:




Question 5
An essential item in a fieldwork first aid kit is:





Question 6

Tidal flats similar to those shown in this image hold risks because:




Question 7







Question 8
Always wear ear defenders when you are close to noisy
plant in working quarries because there is risk of:




Question 9
A mobile phone may be useful when you are doing fieldwork, but remember that:




Question 10
Blasting occurs in most hard rock quarries like Bardon Hill Quarry (shown in this
image). When blasting takes place there is risk of major physical injury resulting from:





Question 11

This is a view looking towards Llyn Ogwen in Snowdonia. If you are undertaking fieldwork in
this area it is always essential to wear:




Question 12
There is special risk in military training areas in coastal areas of:




Question 13
When you are working in upland areas it is essential that you:




Question 14
The International Distress Signal is:





Question 15
This photograph shows a
coastal area near Amroth,
Pembrokeshire. The main
hazard here is the:





Question 16
Insect bites can be a problem when working in the field, particularly in northern latitudes and
in upland or marshy areas. The best precaution to take to prevent or reduce the risk of harm is to:




Question 17
When you are doing fieldwork in coastal areas and are
likely to be working on a wavecut platform like the one
illustrated here you should always plan to work:





Question 18
Quicksand is a hazard in some coastal areas. If you get stuck in quicksand the first thing that you
should do is:




Question 19

Wherever possible you should avoid crossing a river, especially if you are alone. If it is essential to
ford or cross a river you should loosen the shoulder straps and undo the waist strap of your
rucksack because:




Question 20
If you are working in a quarry like
the quarry shown in this image you must: